Comparing OpenAI’s O1 and DeepSeek’s R1 for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Which One Is Better?
OpenAI’s O1 and DeepSeek’s R1 are advancing Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), but which is better? This comparison explores their strengths, differences, and ideal use cases to help you choose the best AI model for your needs.

AI is evolving fast. Like, really fast.
One moment, we’re amazed at how ChatGPT can draft emails, and the next, we’re debating which AI model rules the Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) game. And now, two giants—OpenAI’s O1 and DeepSeek’s R1—are at the center of that debate.
Think of it as a showdown:
- O1 is like the master strategist—meticulous, structured, and brilliant at breaking down complex problems.
- R1 is the agile problem-solver—quick on its feet, adaptive, and designed to thrive in dynamic environments.
But here’s the real question: Which one is better for your needs?
You’ve probably heard about OpenAI’s O1 shining in research, coding, and structured problem-solving. Meanwhile, DeepSeek’s R1 is making waves with its reinforcement learning approach, refining its reasoning skills with every challenge.
So, let’s cut through the noise. In this blog, we’re putting these two powerhouses under the microscope to see which one truly dominates the RAG landscape—not just in theory, but in real-world performance.
What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is reshaping AI applications that rely on real-time information retrieval and synthesis. From financial forecasting to medical diagnostics, the effectiveness of a RAG model depends on its ability to retrieve precise data and generate insightful responses without hallucinations.
At its core, RAG combines two components:
- The Retriever – Finds relevant external data.
- The Generator – Uses the retrieved data to produce informed, coherent responses.
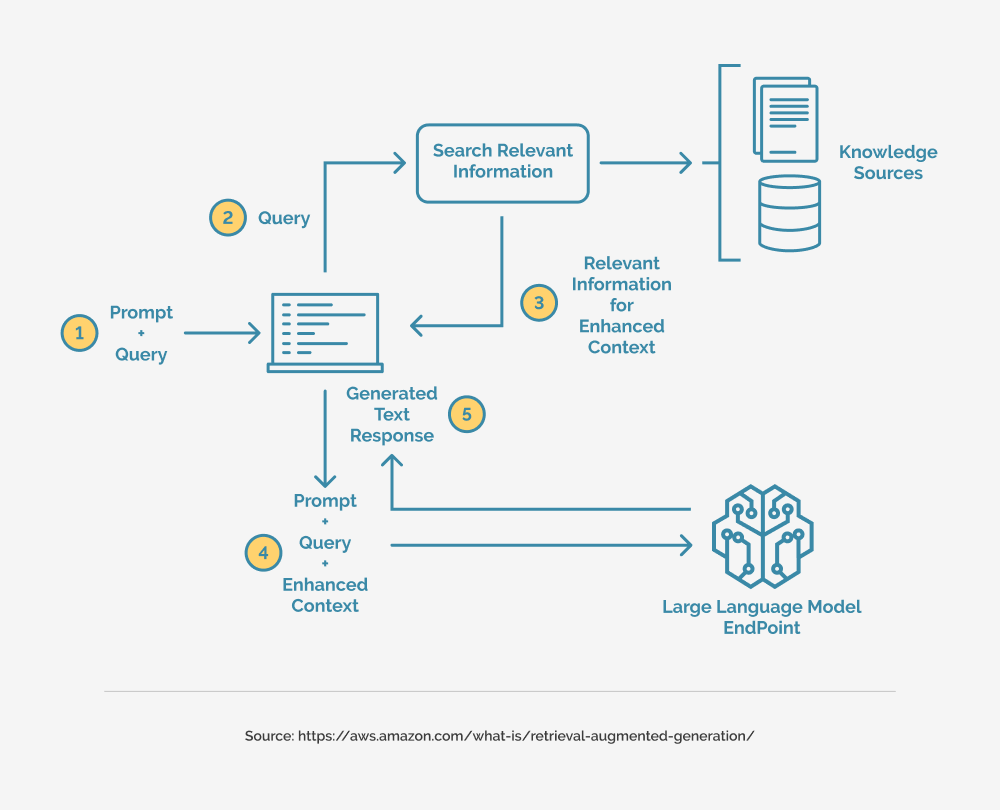
Two leading models in this space—OpenAI’s O1 and DeepSeek’s R1—offer distinct approaches to retrieval, training, and scalability. But which one truly delivers better performance, cost-efficiency, and adaptability for your needs?
While much focus is placed on the generation aspect, the retriever’s efficiency is just as critical—especially for real-time applications like fraud detection, legal analysis, and supply chain optimization.
A model’s retrieval precision and indexing strategy dictate how well it can source the most relevant information. OpenAI’s O1 and DeepSeek’s R1 differ significantly in this aspect, making it essential to understand their respective architectures.
This comparison breaks down their strengths, weaknesses, and ideal use cases, helping you decide whether O1 or R1 is the better fit for your application.
Key Differences Between OpenAI’s O1 and DeepSeek’s R1
How They Find and Understand Information
The biggest difference between OpenAI’s O1 and DeepSeek’s R1 is how they search for and process information.
How O1 Works
O1 is built to organize and find information in a structured way using something called hierarchical indexing. This makes it great at handling complex problems and reducing mistakes.
How R1 Works
R1, on the other hand, learns from experience using reinforcement learning. This allows it to get better over time and adjust to different situations. It's particularly useful for tasks that change often, like fraud detection and financial forecasting.
If you need a model that is great at deep research and structured tasks, O1 is the better choice. But if you want something that adapts and improves with time, R1 is the way to go.
How They Learn
The way these models are trained also makes them very different.
O1 Learns from Human Examples
O1 learns from carefully selected data provided by human trainers. This makes it highly reliable for things like legal analysis, academic research, and medical studies.
R1 Learns from Experience
R1 doesn’t rely as much on human-curated examples. Instead, it learns from experience using a special method called Guaranteed Relevance Policy Optimization (GRPO). This helps it improve how it finds and processes information on its own.
If you need an AI that is deeply trained on facts and structured knowledge, O1 is better. But if you need one that adapts to new data and evolving situations, R1 is the smarter choice.
How Much Computing Power They Need
A big consideration when choosing between these models is how much computing power and resources they require.
O1 Needs More Power
O1 is a powerful model, but that power comes at a cost. It requires a lot of computing resources, making it ideal for big companies and research labs that have access to high-performance computers.
R1 Is More Efficient
R1, on the other hand, is designed to be efficient. It uses a method called Mixture of Experts (MoE), which activates only the parts of the AI that are needed at a given time. This helps reduce energy use and makes it more accessible for startups and businesses with smaller budgets.
If you have a high-powered computing setup and need maximum performance, O1 is a great choice. But if you need something more cost-effective and energy-efficient, R1 is the better option.
Where They Work Best
Each model is designed for different kinds of tasks.
O1 Is Great For:
- Scientific research (helping researchers test ideas and analyze data)
- Legal work (reading and analyzing contracts and case law)
- Medical applications (supporting doctors by analyzing patient records and medical studies)
R1 Is Great For:
- Fraud detection (finding unusual patterns in financial transactions)
- Supply chain optimization (predicting delays and improving logistics)
- Financial forecasting (helping businesses predict market trends and risks)
If your work requires deep analysis and fact-based research, O1 is a better fit. But if you need an AI that works in fast-moving, data-driven environments, R1 is the stronger choice.
How Good They Are at Solving Problems
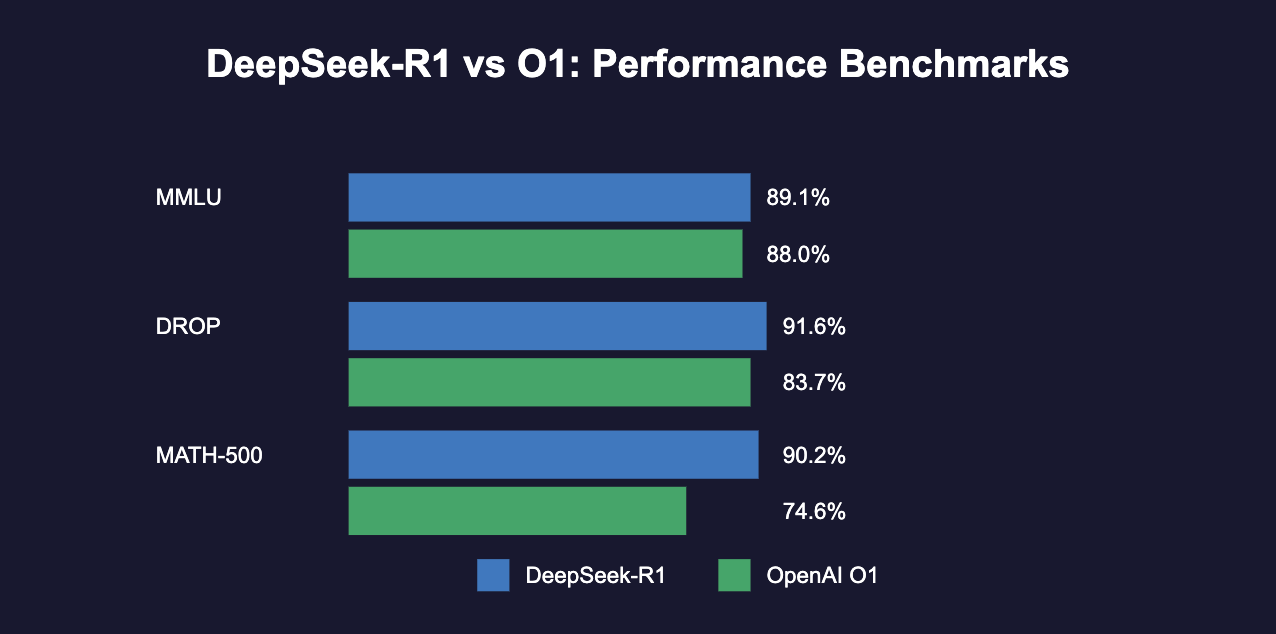
According to a detailed benchmark comparison;
O1 Is Great for General Thinking
O1 scores 91.8% on the MMLU test, which means it’s excellent at answering a wide variety of questions and reasoning through complex topics.
R1 Is Great for Math and Problem-Solving
R1 scores 97.3% on the MATH-500 test, which makes it better at solving math-heavy problems and logical reasoning tasks.
Which One Is More Cost-Effective?
R1 is more efficient and uses less computing power, making it cheaper to run. O1 is more powerful but requires expensive hardware to perform at its best.
If you need an AI that excels at general problem-solving and reasoning, O1 is the better option. If you need something strong in math, logic, and cost-saving, R1 is a great choice.
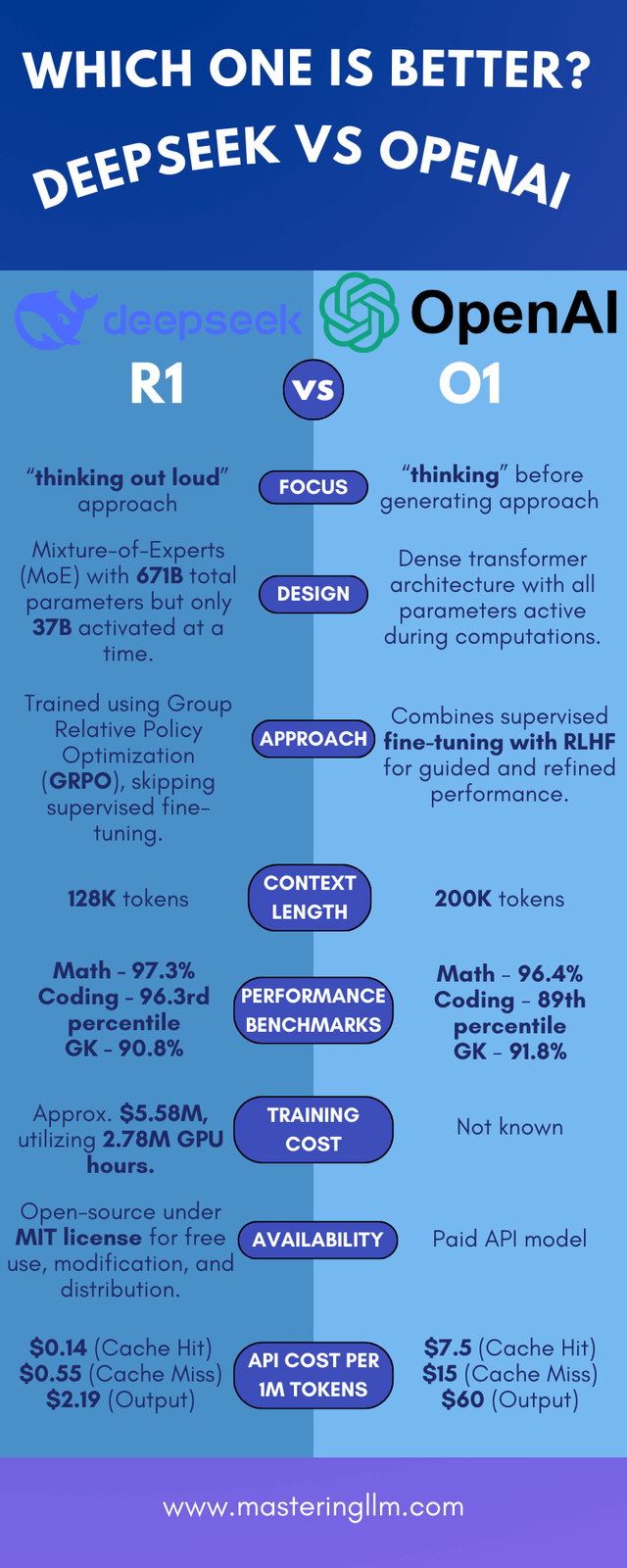
Strengths and Weaknesses
Strengths of O1:
- Highly accurate and reliable
- Handles large amounts of text and images
- Excellent for deep research and structured problem-solving
Weaknesses of O1:
- Expensive to run and requires a lot of computing power
- Less flexible for industry-specific customization
Strengths of R1:
- Cost-effective and energy-efficient
- Can be adapted for specific industries
- Open-source, meaning it can be improved by developers worldwide
Weaknesses of R1:
- Less generalizable across different subjects
- Performance can vary because it depends on community updates
Which One Should You Choose?
Choose O1 If:
- You work in law, healthcare, or scientific research
- You need a highly accurate and structured AI
- You have strong computing resources and can handle the costs
Choose R1 If:
- You need a more affordable AI that works quickly
- You work in fraud detection, supply chain, or finance
- You want an AI that can adapt and learn on its own
Best Option? Maybe Both
For some businesses, the best choice isn’t one or the other—it’s both.
- O1 is great for structured, high-stakes work that requires precision.
- R1 is better for real-time, cost-effective decision-making.
Final Thoughts
There’s no one-size-fits-all AI. The right choice depends on your needs, budget, and resources. Understanding what you need from an AI will help you make the best decision.


