RAG vs Graph RAG: Which One is the Real Game-Changer for Knowledge Retrieval?
Graph RAG came to the party with math. RAG brought street smarts. Who’s the real MVP?

In the race to revolutionize knowledge retrieval, what if the real game-changer isn’t just smarter algorithms but a shift in how we connect and contextualize data? The stakes? Transforming AI’s accuracy and relevance forever.
The Evolving Landscape of Knowledge Retrieval
As data complexity grows, traditional retrieval methods often falter in delivering nuanced, context-rich insights. Enter RAG and Graph RAG, which redefine how AI systems interact with structured and unstructured data.
Graph RAG, for instance, leverages knowledge graphs to map intricate relationships between entities, enabling multi-hop reasoning. This approach excels in domains like healthcare, where linking patient histories with treatment outcomes can uncover life-saving patterns. Meanwhile, RAG’s vector similarity search thrives in scenarios requiring rapid, large-scale unstructured data processing, such as real-time customer support.
However, the real game-changer lies in hybrid models that combine these strengths. By integrating vector databases with knowledge graphs, organizations can achieve both speed and depth, addressing complex queries without sacrificing efficiency.
This evolution challenges the assumption that one-size-fits-all solutions suffice. Instead, it underscores the importance of tailoring retrieval strategies to specific use cases, paving the way for more adaptive, intelligent systems.
The Rise of RAG and Graph RAG in NLP
Graph RAG’s semantic structuring transforms NLP by enabling explainable AI, crucial in regulated industries like finance. Unlike traditional RAG, it excels in multi-step reasoning, linking disparate data for actionable insights.
Understanding Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
RAG bridges retrieval systems and language models, dynamically sourcing relevant data to enhance responses. For instance, in e-commerce, RAG personalizes recommendations by integrating user history with real-time product trends, boosting engagement and sales.
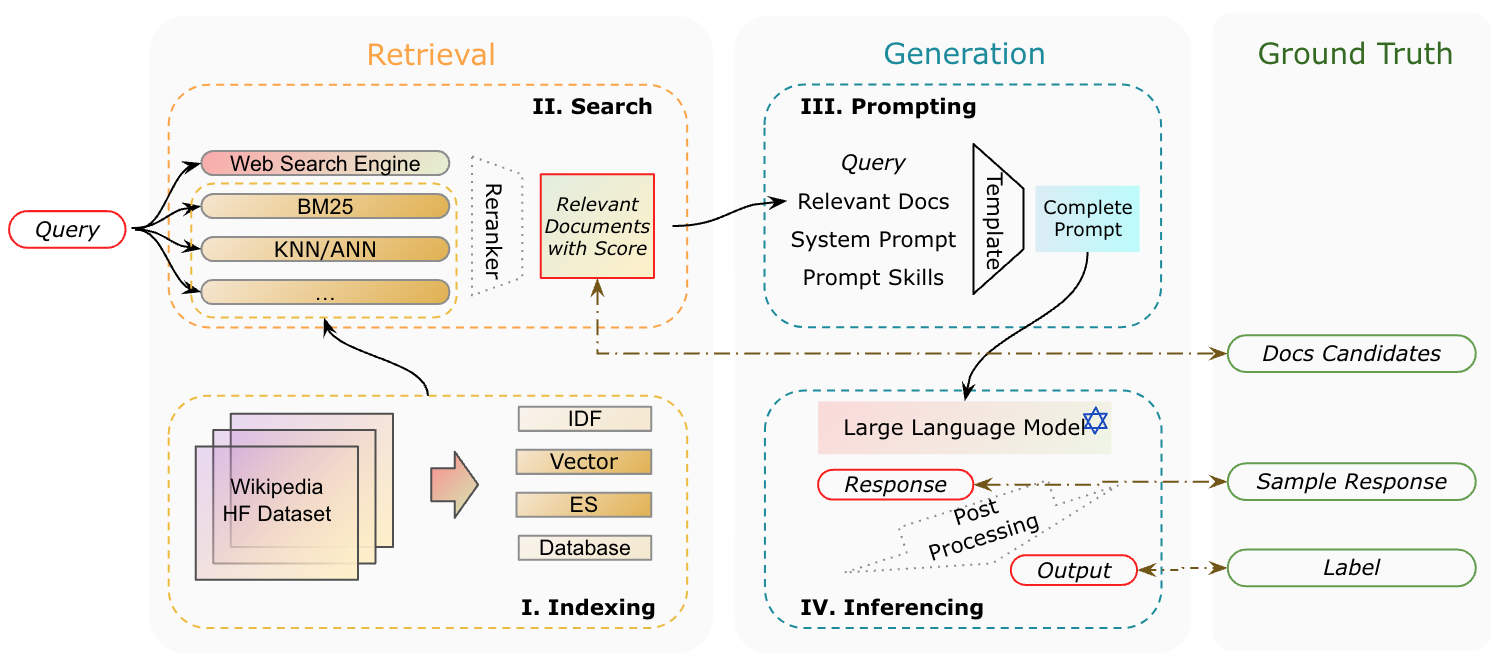
Core Principles and Architecture of RAG
The fusion module in RAG seamlessly integrates retrieved data into language models, enabling context-aware outputs. In healthcare, it synthesizes patient records and clinical guidelines, delivering precise, personalized treatment recommendations while reducing diagnostic errors.
Enhancing Knowledge Retrieval with RAG
RAG excels by dynamically integrating multi-source data, such as combining real-time analytics with historical records. In finance, this approach uncovers hidden market trends, enabling smarter investment strategies and reducing decision-making risks.
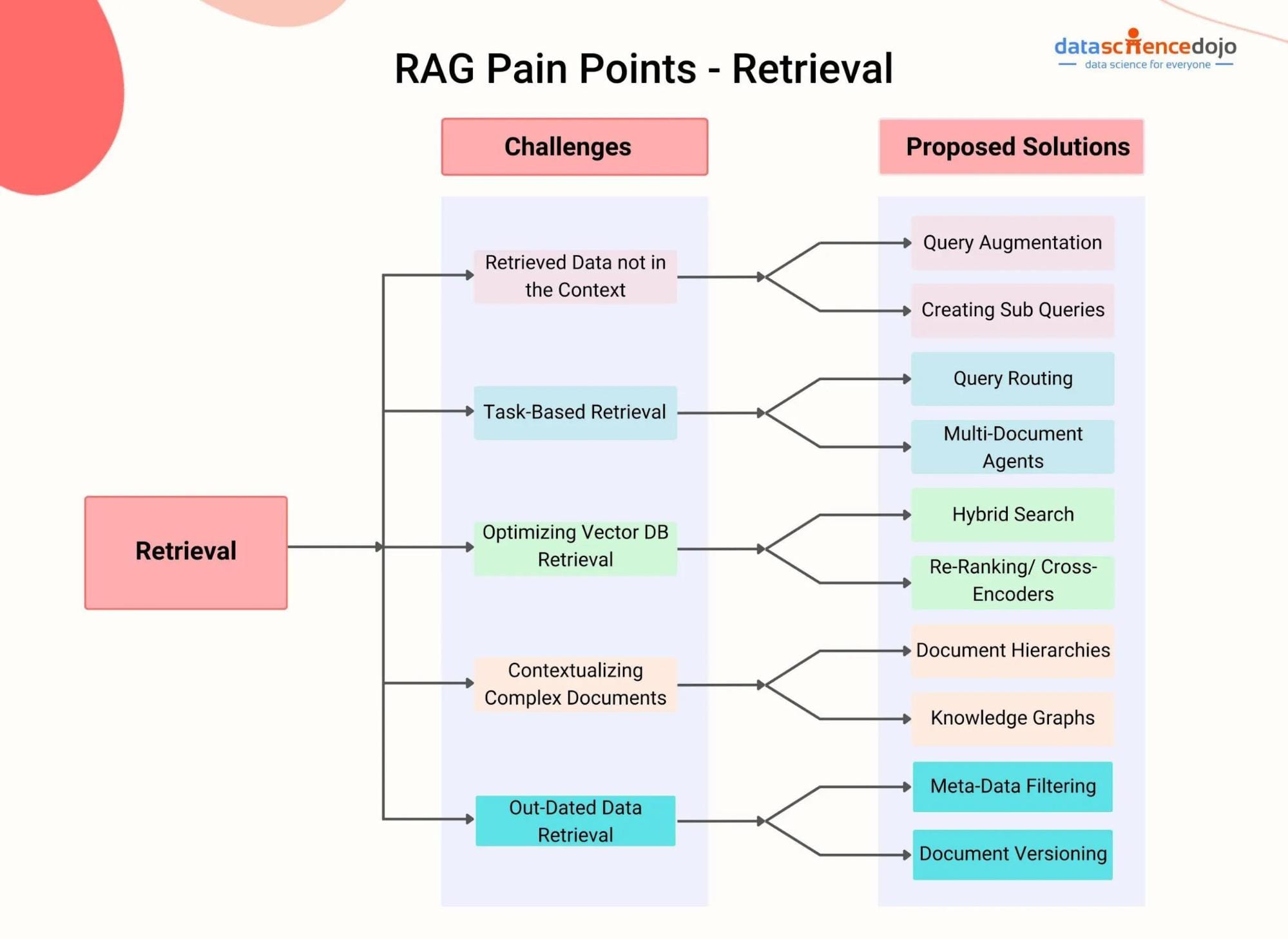
Limitations and Challenges in Implementing RAG
Scalability remains a hurdle as data volumes grow exponentially. Optimizing retrieval mechanisms for low-latency performance in large datasets is critical, especially in real-time applications like fraud detection or personalized e-commerce recommendations.
Exploring Graph RAG
Graph RAG leverages knowledge graphs to uncover hidden relationships, enabling multi-hop reasoning. For instance, in healthcare, it synthesizes patient histories and clinical guidelines, offering context-rich insights that surpass traditional RAG’s linear retrieval methods.
Leveraging Knowledge Graphs in Retrieval
Knowledge graphs excel in semantic disambiguation, linking entities across datasets. For example, in financial analysis, they connect market trends with historical data, enabling predictive insights. This bridges gaps traditional vector searches often overlook.
Mechanics of Graph RAG Models
Graph RAG integrates graph traversal algorithms with retrieval systems, enabling multi-step reasoning. In legal research, it maps precedents to statutes, uncovering nuanced relationships. This approach redefines contextual depth, fostering breakthroughs in complex decision-making processes.
Assessing the Benefits and Limitations of Graph RAG
Graph RAG’s real-time updates enhance decision-making in dynamic fields like healthcare. However, scalability challenges arise with large graphs, demanding optimized algorithms. Future innovations could integrate multimodal data for richer, actionable insights.
Comparative Analysis: RAG vs Graph RAG
Graph RAG excels in multi-hop reasoning, connecting disparate data for richer insights, as seen in LinkedIn’s 62.5% reduction in ticket resolution time. Traditional RAG, while faster, struggles with contextual depth in complex queries.
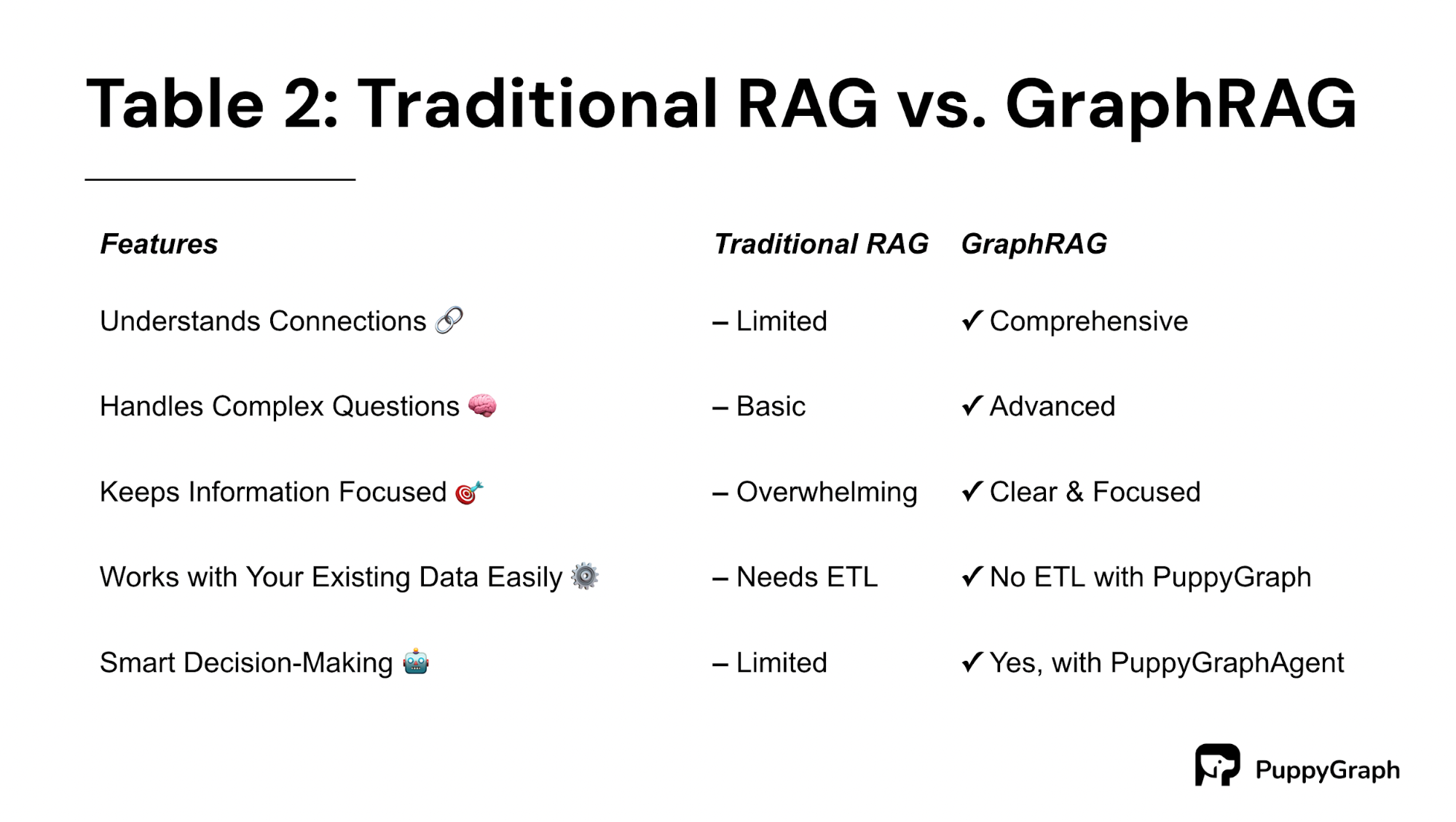
Key Technical Differences Between RAG and Graph RAG
Graph RAG’s knowledge graph integration enables semantic disambiguation, crucial for ambiguous queries. For instance, in fraud detection, it identifies hidden patterns across datasets, unlike RAG’s reliance on vector similarity, which limits contextual depth.
Comparative Performance Evaluation
Graph RAG outperforms RAG in RobustQA benchmarks, scoring 86.31% versus 72.36%. Its multi-hop reasoning reduces hallucinations, making it ideal for risk assessment and fraud detection in high-stakes industries like finance.
Domain-Specific Applications and Suitability
Graph RAG excels in legal research, linking statutes, precedents, and case law for comprehensive analysis. Its semantic structuring uncovers hidden relationships, enabling attorneys to craft stronger arguments and predict case outcomes effectively.
Practical Implementations and Case Studies
A veterinary startup used Graph RAG to align animal breeds with diseases, boosting diagnostic accuracy. Similarly, RAG in e-commerce personalized recommendations by analyzing user trends, proving its adaptability across diverse industries.
Deployment of RAG in Enterprise Solutions
Enterprise RAG thrives by harmonizing fragmented data from legacy systems and cloud platforms. For instance, financial firms leverage it to unify compliance data, ensuring real-time accuracy while reducing manual oversight and operational bottlenecks.
Graph RAG Applications in Complex Systems
Graph RAG excels in scientific research, mapping interdisciplinary connections. For example, universities use it to link papers, authors, and concepts, uncovering hidden trends and fostering collaboration across traditionally siloed disciplines.
Case Study: Comparing Outcomes in Real-World Scenarios
Graph RAG reduced LinkedIn’s ticket resolution time from 40 to 15 hours by enabling multi-hop reasoning, prioritizing relevant pathways, and integrating structured data—highlighting its transformative potential in streamlining complex workflows.
Emerging Trends and Future Directions
Hybrid models combining Graph RAG with multimodal data are reshaping industries. For instance, healthcare systems integrate patient histories with imaging data, enabling context-rich diagnostics. This trend underscores the shift toward holistic, adaptive AI solutions.
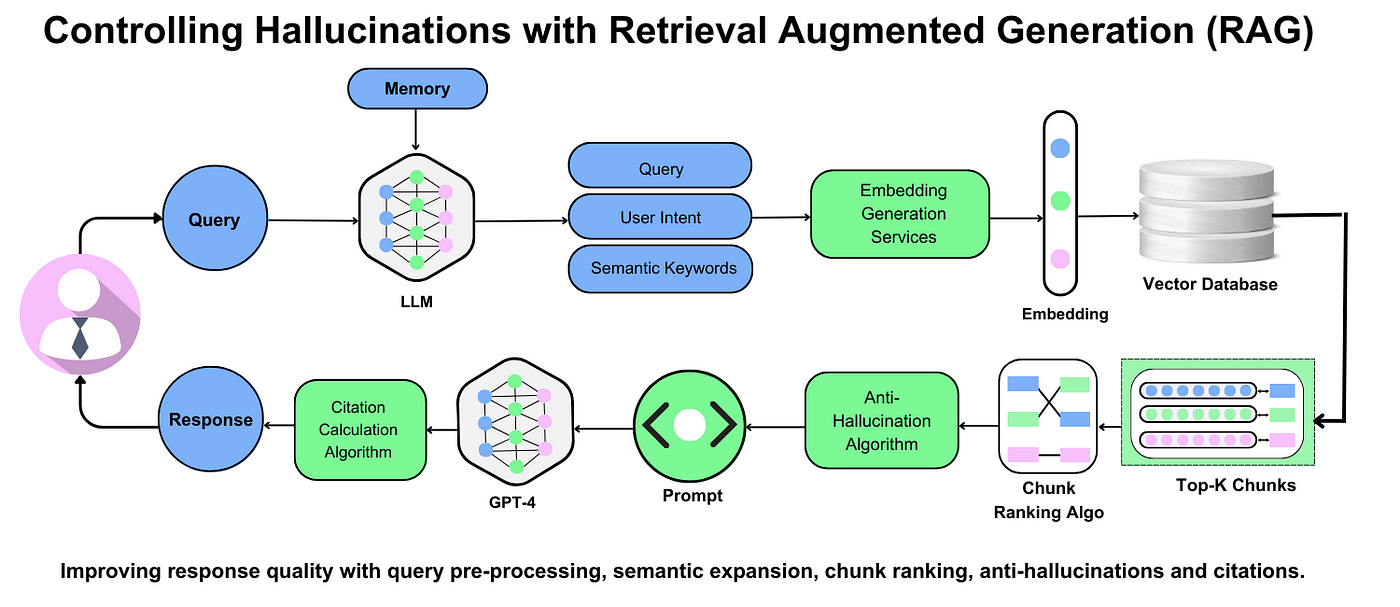
Innovations in Retrieval-Augmented Models
Dynamic meta-knowledge summaries now refine retrieval by clustering related documents, boosting contextual accuracy. For example, legal AI tools map precedents efficiently, reducing research time—paving the way for domain-specific, adaptive retrieval frameworks.
Synergies with AI, Machine Learning, and Beyond
Integrating Graph RAG with reinforcement learning optimizes decision-making in autonomous systems. For instance, supply chain AI leverages multi-hop reasoning to predict disruptions, aligning operational efficiency with real-time adaptability across industries.
Future Research Opportunities and Challenges
Exploring multimodal RAG integration—combining text, images, and audio—can revolutionize contextual understanding. For example, healthcare AI could synthesize medical imaging with patient history, enabling holistic diagnostics and advancing precision medicine through adaptive learning frameworks.
FAQs:
What are the key differences between RAG and Graph RAG in knowledge retrieval?
RAG primarily relies on unstructured text and vector similarity for retrieval, offering speed and simplicity. In contrast, Graph RAG integrates structured knowledge graphs, enabling enhanced contextual understanding, multi-hop reasoning, and precise handling of complex queries.
How does Graph RAG improve multi-hop reasoning compared to traditional RAG?
Graph RAG leverages knowledge graphs to traverse relationships between entities, enabling logical connections across multiple data points. This structured approach allows deeper insights and accurate responses, surpassing traditional RAG’s reliance on vector similarity for reasoning.
What are the primary use cases for RAG and Graph RAG in various industries?
RAG excels in e-commerce for personalized recommendations and customer support automation, while Graph RAG thrives in healthcare for clinical decision-making and finance for fraud detection, leveraging its structured, relationship-driven insights.
What challenges arise when implementing Graph RAG for large-scale datasets?
Implementing Graph RAG for large-scale datasets presents challenges such as ensuring scalability, maintaining data quality, and optimizing query performance. The complexity of constructing and updating knowledge graphs, along with managing dynamic data, requires advanced indexing and efficient algorithms.
How do knowledge graphs enhance the performance of Graph RAG systems?
Knowledge graphs enhance the performance of Graph RAG systems by providing structured, interconnected data that improves contextual understanding, reduces hallucinations, and enables multi-hop reasoning. This results in more accurate, reliable, and contextually relevant responses for complex queries.
Conclusion
Graph RAG emerges as a transformative force in knowledge retrieval, particularly for industries requiring multi-hop reasoning and contextual depth. For instance, in healthcare, it synthesizes patient histories with clinical data, enabling precise diagnostics. Unlike RAG, which excels in speed and simplicity for unstructured data, Graph RAG thrives on structured relationships, offering nuanced insights. However, scalability challenges persist, especially with large datasets. Think of RAG as a sprinter—fast but limited in endurance—while Graph RAG is a marathoner, excelling in complex, long-term tasks. As industries increasingly demand explainable AI, Graph RAG’s structured approach positions it as a game-changer, bridging gaps traditional methods often miss.
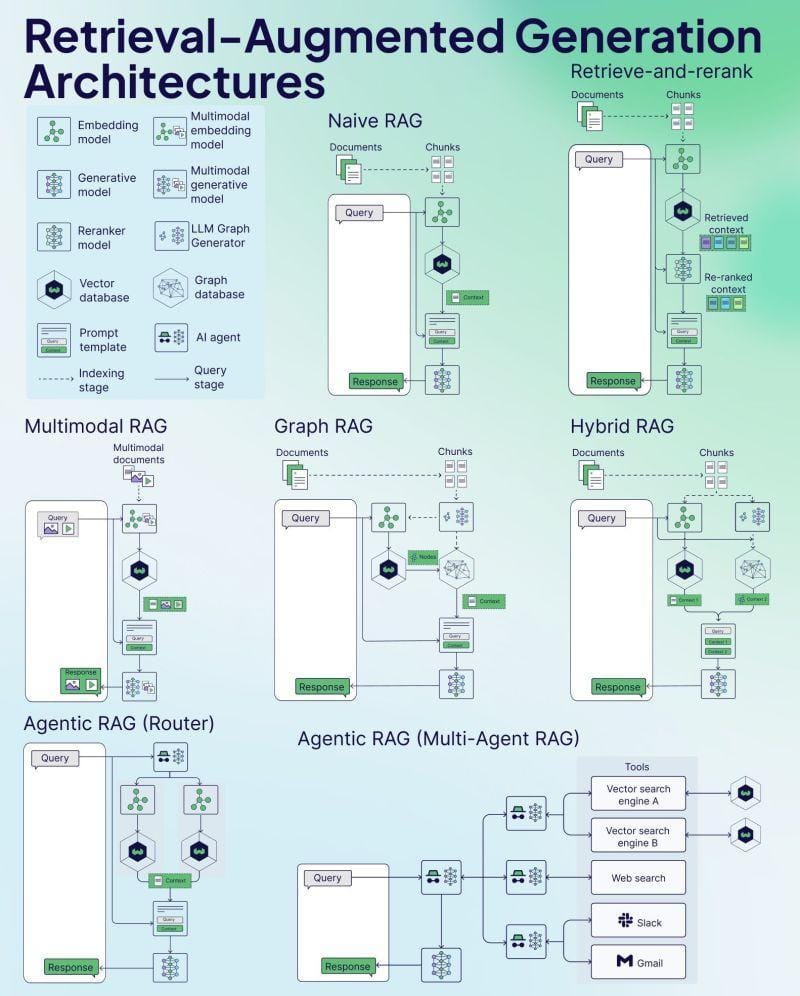
Synthesizing Comparative Insights
Graph RAG’s multi-hop reasoning redefines complex problem-solving by connecting disparate data points. For example, in fraud detection, it identifies hidden patterns across financial networks, outperforming RAG’s linear retrieval. This approach mirrors neural network backpropagation, where layered reasoning enhances precision. Lesser-known factors, like graph traversal algorithms, significantly influence outcomes by prioritizing relevant pathways. Actionable insight: industries should invest in dynamic graph updates to maintain real-time accuracy, ensuring scalability and relevance in rapidly evolving domains.
Predicting the Trajectory of Knowledge Retrieval Technologies
Future advancements hinge on multimodal integration, combining text, images, and real-time data streams. For instance, healthcare could leverage Graph RAG with genomic data to predict diseases. Actionable insight: prioritize adaptive graph architectures for scalability.

